
During brain formation, newly generated neurons in the proliferative region migrate to their final destinations. For instance, the mammalian brain has a six-layered structure, while the avian brains consist of compartmentalized nuclear slabs. These results indicate that species-specific microenvironments with distinct mechanical properties emerging during development might contribute to the formation of brain structures with unique morphology.Īlthough the vast majority of molecular machinery to generate neurons from progenitors are commonly conserved in amniotes ( Englund et al., 2005 Martínez-Cerdeño et al., 2016 Nomura et al., 2016 Turrero García et al., 2016 Yamashita et al., 2018), the alignment of neurons in matured brains exhibits remarkable diversity ( Medina and Abellán, 2009 Jarvis et al., 2013 Puelles et al., 2017 Cárdenas and Borrell, 2019 Pessoa et al., 2019). The embryonic chick and matured turtle pallia showed gradually increasing stiffness along the apico-basal tissue axis, the lowest region at the most apical region, while the ferret pallium exhibited a catenary pattern, that is, higher in the ventricular zone, the inner subventricular zone, and the cortical plate and the lowest in the outer subventricular zone. We found stage-dependent and species-specific stiffness in pallia among amniotes. We also measured brain stiffness in other amniotes (chick, turtle, and ferret) following glyoxal fixation. Based on this method, we found that the homologous brain regions between mice and songbirds exhibited different stiffness patterns. Notably, brain tissue fixed by glyoxal remained much softer than PFA-fixed brains, and it can maintain the relative stiffness profiles of various brain regions.
A comparison of embryonic and juvenile mouse and songbird brain tissue revealed that glyoxal fixation can maintain brain structure as well as paraformaldehyde (PFA) fixation. For a systematic measurement of the brain stiffness of remotely maintained animals, we developed a novel strategy of tissue-stiffness measurement using glyoxal as a fixative combined with atomic force microscopy. To address this point, a comparative analysis of mechanical properties using several animals is required. However, little is known about the correlation between mechanical properties and species-specific brain structures. Recent studies have indicated that differences in the mechanical properties of tissue may result in the dynamic deformation of brain structure, such as folding. 3RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research, Kobe, Japanīrain structures are diverse among species despite the essential molecular machinery of neurogenesis being common.2Developmental Neurobiology, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan.1Korea Brain Research Institute, Daegu, South Korea.Then we computed z-scores for each subject’s data and compared the groups using MANOVA with p value set at 0.05, corrected for multiple comparisons, considering group and visit as the independent variables.Misato Iwashita 1*, Tadashi Nomura 2, Taeko Suetsugu 3, Fumio Matsuzaki 3, Satoshi Kojima 1 and Yoichi Kosodo 1* To perform a quantitative analysis across the two groups, we first used the Johns Hopkins University tractography atlas to define 20 regions of interest (ROI), and the scans from the control subjects to create a reference database that included the mean and standard deviation values in each ROI.
#FA THRESHOLD IN MEDINRIA FOR MICE BRAIN REGISTRATION#
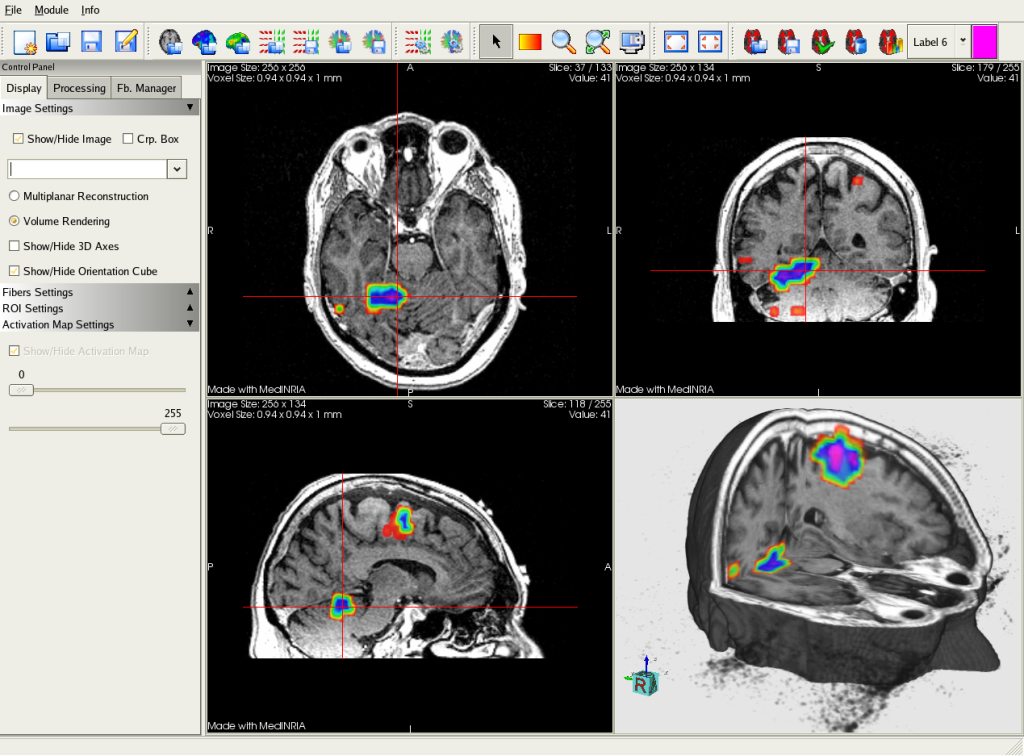
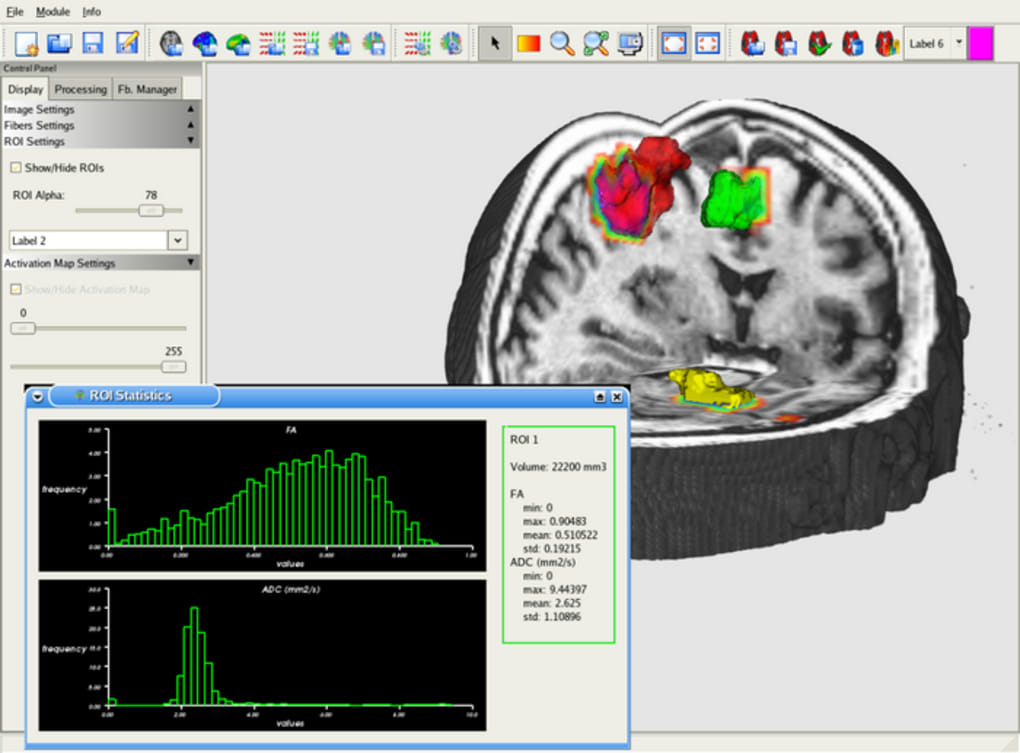
An affine linear registration routine part of FSL was also used to align the 32 images to the reference image.įor each DTI dataset, diffusion Fractional Anisotropy (FA), Mean Diffusivity (MD) or Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC), and probabilistic tractography were estimated using FSL and the software package MedInria, with an FA threshold of 200, a minimum length for the detected fibers of 20 mm, and volume sampling every 5 voxels. Image distortions, resulting from susceptibility-induced and by eddy current-induced off-resonance fields, were corrected using routines from the software package FSL. Images were acquired on three different visits, two weeks and four weeks, respectively, after the first recording, using a 3.0 T. Thirteen acute mTBI patients 18-50 years of age and seven age- and sex-matched controls with no head injury were recruited from the emergency department of Huntington Memorial Hospital in Pasadena, CA. In this study we investigated whether Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) could be used to assess recovery in patients with mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
